Microorganism
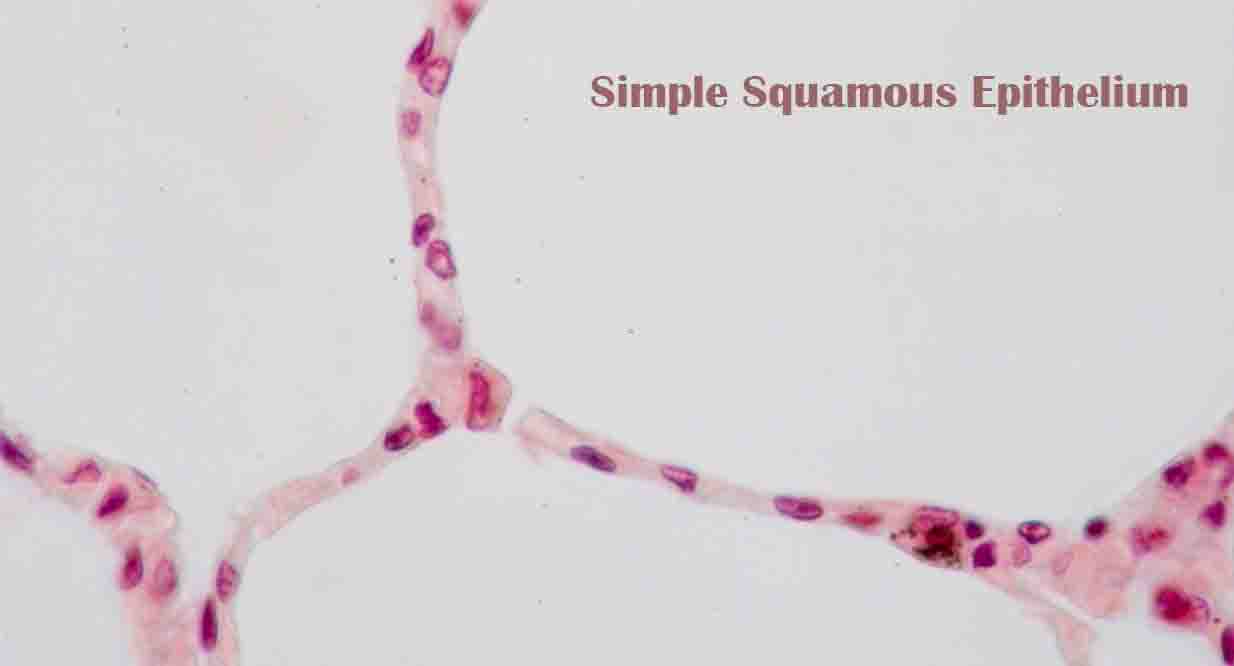
Microorganism Definition A microorganism is a living thing that is too small to be seen with the naked eye. Examples of microorganisms include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa, and microscopic animals such as the dust mite. These microorganisms have been often under-appreciated and under-studied. Indeed, until Anton von Leeuwenhoek invented the microscope, we did not know … Read more